Welcome to the world of vegan cooking, where culinary possibilities are as vast as well as exciting as they are delicious. Whether you’re a committed vegan or just curious about plant-based cooking, our Ultimate Guide to Vegan Cooking is your guide to a fun, compassionate and healthy culinary journey.
Vegan cooking is not boring at all, despite what some people may think. Hence, It’s actually quite exciting! There are clever tricks and special ingredients that make vegan food taste just as good, if not better, than regular non-vegan food. Our guide will show you that vegan cooking is full of delicious and fulfilling dishes. These dishes not only make your taste buds happy but also match your values of being kind to animals and the environment.
This guide will give you recipes and things you need for your vegan cooking. Thus, we want to make your vegan journey easy, fun, and yummy. So, put on your apron, and let’s explore a world of tasty sweets that are good for your taste buds and the planet.
Plant-Based Nutrition Guide for Vegan Cooking
Before we dive into the kitchen and start cooking, it’s essential to consider some key nutrition factors. These considerations will ensure that your vegan meals are not only delicious but also nutritionally balanced. Furthermore, to help you achieve this, we’ve prepared a list of foods to have in your pantry that will provide you with all the essential nutrients that you should pay attention to on a vegan diet.
Protein: beans, legumes, tofu, tempeh, seitan, and meat alternatives.
Calcium: fortified vegetable milk, tofu, leafy greens, and almonds.
Iron: Potatoes, legumes, tofu, quinoa, and fortified grains.
B12: Consider B12 supplements because these are found primarily in animal products.
Plant-Based Protein
Plant-based protein sources are essential for individuals following a vegan or vegetarian diet, and they can also be a healthy addition to any diet. Explore our table of plant-based protein sources. Furthermore, discover how to use each one effectively:
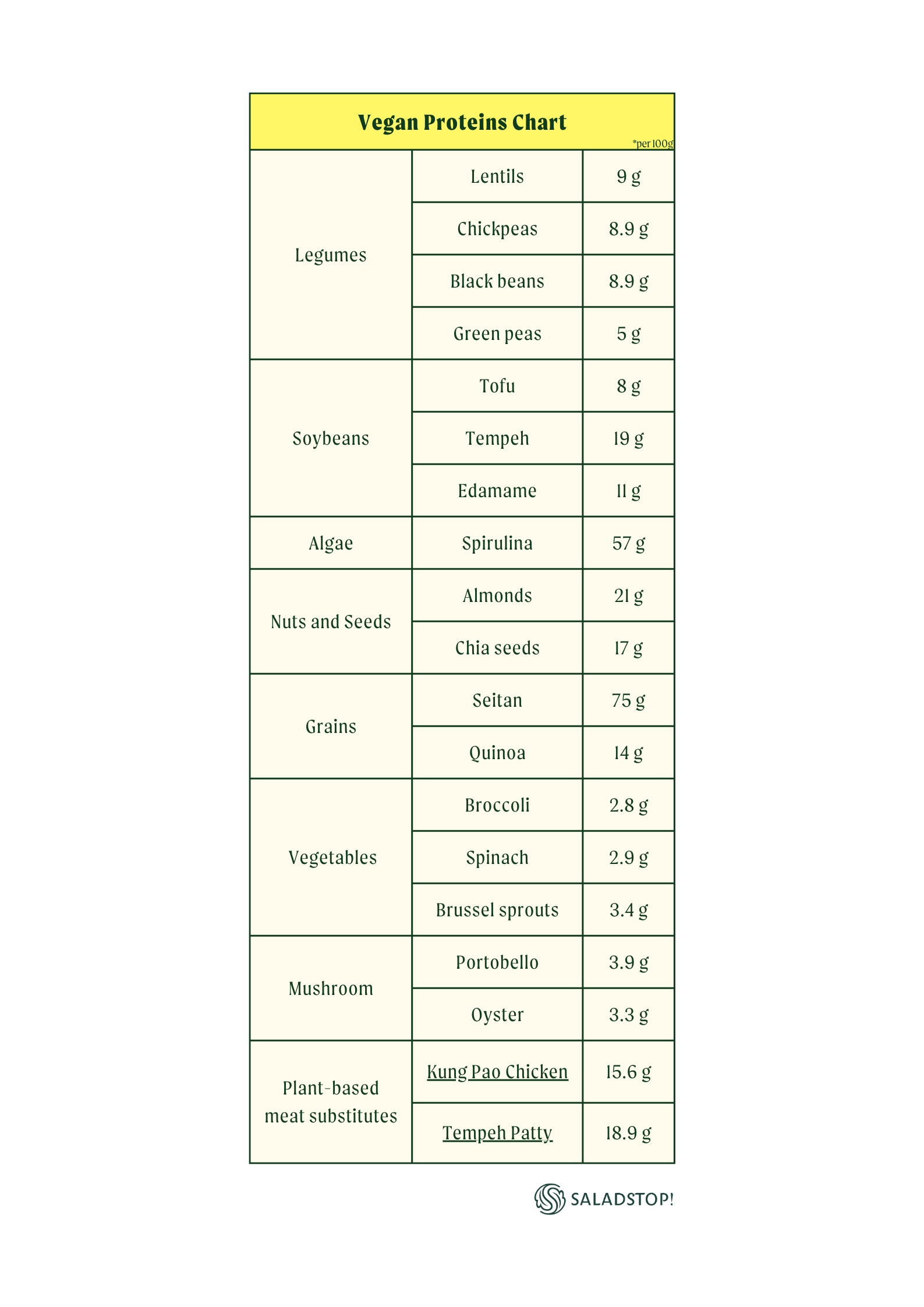
Dairy Alternatives
These dairy alternatives are made from various plant sources and can be used in a wide range of recipes. Moreover, here are some common dairy alternatives:
| Almond Milk | Almond milk is a popular milk substitute which is made from ground almonds and water. Because it has a mild, slightly nutty flavor, it is often used in cereal, coffee, and baking. |
| Soy Milk | Soy milk is made from whole soybean, also has a creamy texture. It’s a versatile milk alternative and is commonly used in both sweet and savory dishes. |
| Oat Milk | Oat milk is made from oats and water, boasting a naturally sweet and creamy taste that is great for coffee, cereal, and baking. |
| Coconut Milk | Coconut milk also used in Asian cuisine, is rich and creamy. It can be used in both sweet and savory recipes, as well as in coffee and smoothies. |
| Rice Milk | Crafted from milled rice, commonly brown rice, rice milk serves as a mild and delicately sweet alternative to traditional dairy milk. Moreover, it is a neutral, slightly sweet milk substitute. |
| Cashew Milk | Cashew milk is made from blended cashews and water, resulting in a creamy, nutty flavor. Thus, making it perfect for desserts. |
| Flax Milk | Flax milk is made from flax seeds and has a mild, slightly nutty taste. Also it’s rich in omega-3 fatty acids and is a good addition to smoothies and cereal. |
| Macadamia Milk | Macadamia milk is made from macadamia nuts and has a rich, buttery flavor. So, It’s a creamy milk alternative for coffee and baking. |
| Plant-Based Yogurt | Plant-based yogurts are made from various ingredients such as almond, coconut, soy, and cashews. Hence, they come in a variety of flavors and can be used as a dairy-free alternative in recipes or enjoyed on their own. |
| Plant-Based Cheese | Plant-based cheeses are made from ingredients like nuts, soy, and tapioca starch. Additionally, they come in a variety of styles and flavors, suitable for melting on pizzas or adding to sandwiches. |
| Plant-Based Butter | Vegan butter is made from oils like coconut or soy and is used as a dairy-free substitute in cooking, baking, and spreading on bread. Furthermore, it provides a versatile option for those seeking plant-based alternatives in their culinary endeavors. |
| Plant-Based Creamers | Creamers made from almond, soy, or coconut are commonly used to replace traditional dairy creamers in coffee and tea. Additionally, these plant-based alternatives offer a rich and creamy texture to enhance your beverages. |
Egg Replacements
These alternatives work well in most recipes that call for eggs. Furthermore, here are some common plant-based egg replacements:
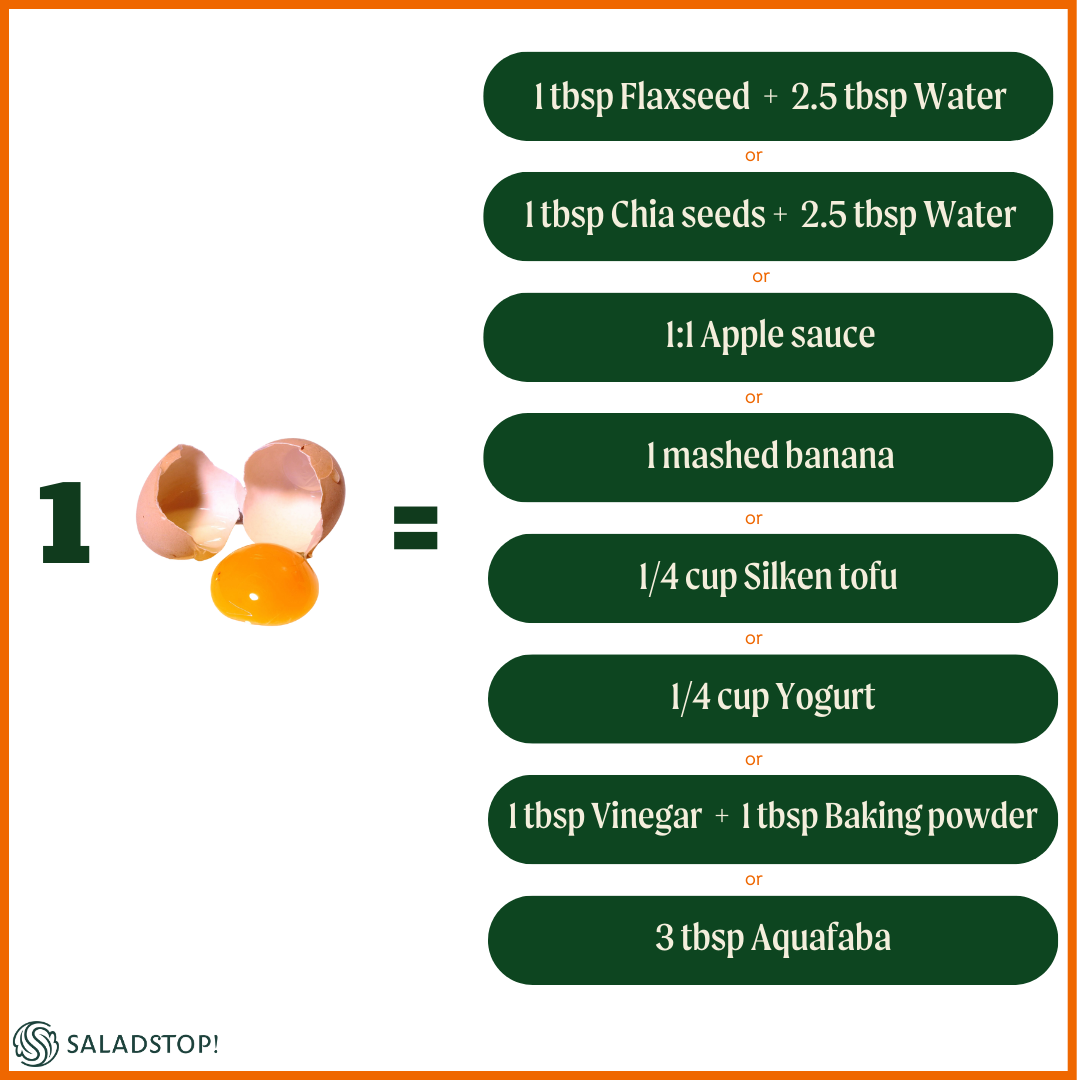
Vegan Substitutes
Here are some popular substitutions for animal-based ingredients:
| Butter Alternatives | Vegan Butter or Margarine: Various brands offer vegan-friendly butter substitutes for baking, spreading, and cooking. Coconut Oil: Unrefined coconut oil can replace butter in many recipes but may impart a subtle coconut flavor. |
| Honey Alternatives | Maple Syrup: You can use this natural sweetener in recipes as a substitute for honey. Agave Nectar: Another liquid sweetener that works as a honey substitute. |
| Gelatin Alternatives | Agar-Agar: Coming from seaweed, agar-agar serves as a replacement for gelatin in recipes that necessitate a gelling agent. Additionally, it is derived from seaweed and can be used as a substitute for gelatin in various recipes. Pectin: Utilized in the preparation of jams and jellies, pectin is a plant-based gelling agent. Furthermore, it is commonly employed in the creation of these fruit spreads. |
| Stock and Broth Alternative | Vegetable Broth: Use vegetable broth instead of meat-based broths for soups and stews. |
| Cream Alternative | Coconut Cream: A sumptuous substitute for heavy cream in recipes is coconut cream. Moreover, it serves as a luscious alternative for recipes that call for heavy cream. |
| Bacon Alternative | Tempeh Bacon: By marinating and pan-frying tempeh slices, you can replicate both the taste and consistency of bacon. Furthermore, this method allows you to achieve a bacon-like flavor and texture with marinated and pan-fried tempeh slices. |
| Milk Chocolate Alternative | Dairy-Free Chocolate: When shopping for chocolate, seek out products labeled as “dairy-free” or “vegan” to use in both baking and snacking. Additionally, ensure that the chocolate you choose is marked as “dairy-free” or “vegan” when purchasing it for baking or snacking purposes. |
| Mayonnaise Alternatives | Vegan Mayonnaise: Numerous brands of vegan mayonnaise can be found at grocery stores. These products are typically crafted by manufacturers using plant-based oils such as soybean or canola, and they frequently possess a flavor closely resembling that of traditional mayonnaise. Furthermore, it’s important to note that there is a wide selection of vegan mayonnaise brands on the market, which are readily available in grocery stores. These products are typically made with plant-based oils like soybean or canola and often closely mimic the taste of traditional mayonnaise. Homemade Vegan Mayo: You can make your own vegan mayonnaise using ingredients like silken tofu, aquafaba (the liquid from a can of chickpeas), cashews, or sunflower seeds. Additionally, these homemade options allow you to control the ingredients and customize the flavor to your liking. |
| Sour Cream Alternatives | Vegan Sour Cream: Many brands offer vegan sour cream made from plant-based ingredients like tofu, cashews, or coconut. Therefore, you can look for these products at health food stores or well-stocked supermarkets. Brands like Tofutti and Follow Your Heart produce vegan sour cream alternatives. Cashew Sour Cream: Combine soaked cashews with lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, water, and a pinch of salt to create a smooth sour cream alternative. Additionally, by blending soaked cashews with lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, water, and a touch of salt, you can make a creamy substitute for sour cream. Tofu Sour Cream: Blend silken tofu with lemon juice, apple cider vinegar, and a pinch of salt until smooth. Adjust the flavors to taste. Coconut Yogurt: Unsweetened coconut yogurt can be a tangy and creamy substitute for sour cream. It works well in both savory and sweet dishes. Almond Milk Yogurt: Unsweetened almond milk yogurt is another dairy-free alternative for sour cream. Some brands produce plain, unsweetened almond yogurt that can mimic the taste and texture of sour cream. |
Remember, transitioning to a vegan diet may take time and effort, but it’s a rewarding and ethical choice that can have a positive impact on your health and the planet. Therefore, the key is to stay informed, experiment in the kitchen, and keep learning about the diverse world of vegan cuisine.

Disclaimer:
At SaladStop! Group, our commitment is to empower every individual with reliable, evidence-based nutritional and wellness guidance. To earn your trust as your ultimate resource for nutritional information, our content undergoes rigorous nutritional scrutiny to ensure its accuracy, whether it’s about our offerings, culinary creations, or services. Please note that all information provided is for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical or nutritional advice.




